what is required for a rocket to lift off into space?
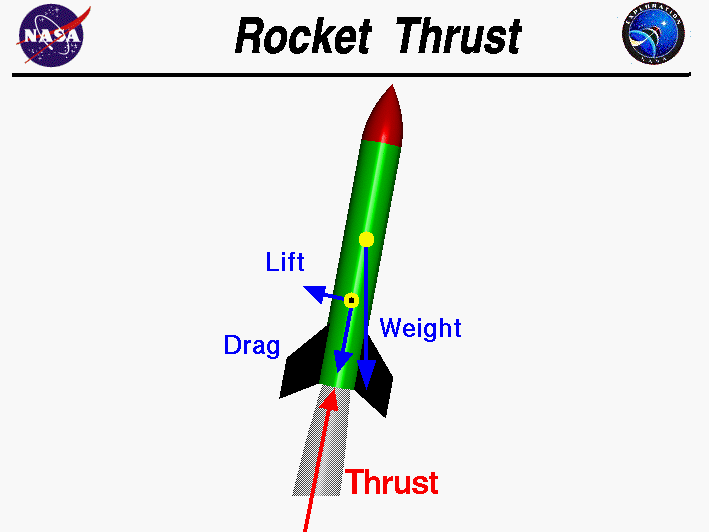
Thrust is the force which moves the rocket through the air, and through space. Thrust is generated by the propulsion system of the rocket through the awarding of Newton'due south tertiary law of motion; For every action in that location is an equal and contrary re-action. In the propulsion system, an engine does work on a gas or liquid, called a working fluid, and accelerates the working fluid through the propulsion system. The re-action to the acceleration of the working fluid produces the thrust force on the engine. The working fluid is expelled from the engine in one management and the thrust forcefulness is applied to the engine in the opposite direction.
Forces are vector quantities having both a magnitude and a direction. When describing the action of forces, one must account for both the magnitude and the management. The direction of the thrust is normally forth the longitudinal axis of the rocket through the rocket eye of gravity. But on some rockets, the exhaust nozzle and the thrust direction tin be rotated, or gimbaled. The rocket tin and so be maneuvered by using the torque about the center of gravity. The magnitude of the thrust can exist determined by the general thrust equation. The magnitude of the thrust depends on the mass flow rate of the working fluid through the engine and the exit velocity and pressure of the working fluid. The efficiency of the propulsion organization is characterized by the specific impulse; the ratio of the amount of thrust produced to the weight flow of the propellants.
All rocket engines produce thrust past accelerating a working fluid. Just at that place are many different ways to produce the acceleration, and many different available working fluids. Let's expect at some of the diverse types of rocket engines and how they produce thrust.
The simplest rocket engine uses air equally the working fluid, and pressure produced by a pump to accelerate the air. This is the blazon of "engine" used in a toy balloon or a stomp rocket. Because the weight flow of air is so small, this type of rocket engine does non produce much thrust. A canteen rocket uses h2o as the working fluid and pressurized air to accelerate the working fluid. Considering h2o is much heavier than air, bottle rockets generate more thrust than stomp rockets.
Model rockets, and most full scale rockets use chemical rocket engines. Chemic rocket engines utilize the combustion of propellants to produce exhaust gases as the working fluid. The high pressures and temperatures of combustion are used to accelerate the exhaust gases through a rocket nozzle to produce thrust. There are ii important parts of a chemical rocket engine; the nozzle, and the propellants. The nozzle design determines the mass flow rate, exhaust velocity, and exit pressure level for a given initial pressure level and temperature. The initial force per unit area and temperature are determined by the chemic properties of the propellants. Propellants are equanimous of a fuel to be burned and an oxidizer, or source of oxygen, for combustion. Under normal temperature weather condition, propellants do non burn, just require some source of heat, or igniter, to initiate combustion. Chemical rocket engines exercise not typically rely on the surrounding atmosphere as a source of oxygen. Therefore, chemical rocket engines can be used in space, where at that place is no temper present.
There are two main types of chemic rocket engines; liquid rockets and solid rockets. In a liquid rocket, the fuel and the oxidizer are stored separately and pumped into the combustion bedchamber of the nozzle where the burning occurs. In a solid rocket, the fuel and oxidizer are mixed together into a solid propellant which is packed into a cylinder. The propellant simply burns on the surface. Then, as the propellant burns, a "flame front" is produced which moves into the propellant. Once the burning starts, it will go along until all the propellant is consumed. With a liquid rocket, yous tin can stop the thrust by turning off the flow of fuel or oxidizer; but with a solid rocket, you must destroy the casing to terminate the engine. Liquid rockets tend to exist heavier and more complex because of the pumps used to motion the fuel and oxidizer, and y'all unremarkably load the fuel and oxidizer into the rocket just before launch. A solid rocket is much easier to handle and can sit down for years before firing.
A new type of rocket engine is the electric engine, also chosen an ion engine. The working fluid for an electric engine is equanimous of very many, but very small, charged particles called ions. The acceleration of the working fluid is produced by electrostatic forces, not by combustion. Ion engines produce very small amounts of thrust, but can produce the thrust for long periods of time because the mass flow rates are very small. Ion engines have very loftier specific impulse when compared to chemic rockets.
Another new blazon of rocket engine is the nuclear thermal engine. In the nuclear thermal engine, a nuclear reactor provides a continuous source of heat which is used to accelerate the working fluid. The working fluid can be whatever gas which is heated as information technology is passed over or through the reactor and exited through the nozzle. The temperature of the exhaust, and the resulting exit velocity, can exist much college than for the typical chemical rocket. The only propellant is the single working fluid, then nuclear rockets are predicted to take very high specific impulse. Nuclear thermal engines are being developed under Project Prometheus.
Guided Tours
Activities:
Rocket Propulsion Activity: Form ix-10
Fundamental Terminology: Grade 10-12
Related Sites:
Rocket Index
Rocket Home
Beginner'due south Guide Home
singletonsherep55.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/k-12/rocket/rktth1.html
Post a Comment for "what is required for a rocket to lift off into space?"